1. During meiosis, the X and Y chromosomes pair as homologs, although there is never any crossing over between them.
If a gamete is produced that contains two Y chromosomes (by mistake), at which division did the nondisjunctional event take place?
|
a. second division
b. first division
c. could have been either
d. the event must have been premeiotic
e. none of these
|
2. Two homologous chromosomes fail to pair during prophase of meiosis. Which of the following is likely to occur as a result?
|
a. Crossing over is eliminated
b. Creates a high probability of nondisjunction
c. both a. and b. are correct
d. the chromosomes fail to replicate
e. The cell fails to divide
|
3. If the F2 of a dihybrid cross gives a 12:3:1 ratio, what will be the ratio of phenotypes if one takes an F1 individual (from the same
cross) and test crosses it?
|
a. 1:1:1:1
b. 3:1
c. 2:1:1
d. 3:3:1
e. 3:1:1
|
4. If a couple has 7 children, what is the probability of their having 3 girls and then having 4 boys?
|
a. 1/2
b. 1/144
c. 1/128
d. 1/256
e. none of these
|
5. If a couple has 7 children, what is the probability of their having 3 girls and 4 boys?
|
a. 1/2
b. 21/128
c. 70/128 align="left" style="margin-top: 0; margin-bottom: 0">
d. 35/128
e. none of these
|
6. If a couple has 7 children, what is the probability of their having 3 or more girls?
|
a. 35/128
b. 70/128
c. 99/128
d. 119/128
e. none of these
|
7. If the following cross is made: AaBbccddEe x aaBbCcDdee
>what is the probability of obtaining an individual that expresses the recessive phenotype for all 5 loci?
|
a. 1/128
b. 1/64
c. 3/64
d. 9/64
e. 27/64
|
8. The ability to taste the compound phenylthiourea is dominant. IF both parents are heterozygous for the taster allele (Tt), what is the probability of having a family of 4 consisting of two tasters and two non-tasters?
|
a. 1/256
b. 6/256
c. 36/256
d. 54/256
e. none of these
|
9. In peas, tall (plant) is dominant to short, and round (seed) is dominant to wrinkled. A plant that is heterozygous for both loci is crossed to an unknown plant. The progeny that result are: 598 tall round: 210 tall wrinkled: 602 short round: and 198 short wrinkled. What was the phenotype of the unknown plant?
|
a. Tall round
b. Tall wrinkled
c. Short round
d. Short wrinkled
e. It cannot be determined
|
10. A tall round pea plant, when allowed to self pollinate, produces a 9:3:3:1 ratio of tall round: tall wrinkled: short round: short wrinkled. What ratio would result if this plant were crossed to a homozygous (true breeding) plant that was short wrinkled?
|
a. 1:1: 1:1 ratio of tall round: tall wrinkled: short round: short wrinkled
b. 1:1 ratio of tall round: tall wrinkled
c. 3:1 ratio of tall round: short wrinkled
d. 3:1 ratio of tall round: tall wrinkled
e. None of these
|
11. In Drosophila, yellow body (y)
is sex linked and recessive. Brown eyes (bw) is autosomal and
recessive. A yellow brown male is crossed to a homozygous
wild-type female producing an F1 in which both males
and females are phenotypically wild-type. The F1 are
inbred to form an F2.At what frequency (of total flies)
would you expect to find a yellow (but not brown) male in the F2.
|
a. 1/16
b.
3/16
c. 4/16
d. 6/16
e. 9/16
|
12. See problem 11.At what frequency would you expect to find a yellow brown female in the F2.
|
a. 1/16
b. 3/16
c. 4/16
d. 6/16
e. none of these
|
13. Cystic fibrosis is inherited as an autosomal recessive. Two parents without cystic fibrosis have two children with cystic fibrosis and three children without. They have come to you for genetic counseling. What is the numerical probability that their next child will have cystic fibrosis?
|
a. 0
b. 16/128
c. 96/256
d. 1/4
e. none of these
|
14. See Problem 13.Their unaffected children are concerned about being heterozygous. What
is the numerical probability that a given unaffected child in the
family is heterozygous?
|
a. 0
b. 2/3
c. 1/3
d. 3/4
e. none of these
|
15. A three generation pedigree for a particular human trait is shown in the following figure:
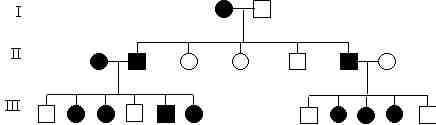
|
Y-linked can be excluded at a glance. What is the mode of inheritance for this trait?
You may assume complete penetrance and full expressivity for the trait.
|
|
a. X linked dominant
b. Autosomal dominant
c. X linked recessive
d. Autosomal recessive
e. either a or b
|
16. Mendel�s laws and where each occurs in Meiosis are as follows:
|
a.
The principle of segregation states that two members of a gene pair segregate from each other in the formation of gametes�demonstrated in Anaphase 1
The principle of independent assortment states that the genes for different traits assort independently of each other (Metaphase 1)
b. The principle of
segregation states that two members of a gene pair segregate
from each other in the formation of gametes� demonstrated
in Metaphase 1
The principle of independent assortment states that the genes for different traits assort independently of each other (anaphase 1)
c. The principle of independent assortment states that two members of a gene pair segregate from each other in the formation of gametes�
demonstrated in Anaphase 1
The principle of segregation states that the genes for different
traits assort independently of each other (Metaphase 1)
|
17. Mendel�s law of independent assortment is violated by
|
a. nondisjunction
b. linkage
c. inversions
d. none of these
|
18. What year (+/- 20 years) did Mendel publish his work?
|
a. 1950
b. 1850
c. 1750
d. 1650
e. 1550 |
19. In Jimsonweed purple flowers
are dominant to white. When a particular purple flowered
Jimsonweed is self-fertilized, there are 28 purple-flowered and 10
white-flowered progeny. What proportion of the purple-flowered
progeny will breed true?
|
a. 3/4
b. 1/2
c. 2/3
d. 1/3
e. 1/4
|
20. The cross of an uncertain genotype with a homozygous recessive genotype at the same locus is a
